

Hero (also known as Heron) was a notable mathematician and mechanical engineer whose many inventions include an early vending machine (perhaps the first) that dispensed holy water when a coin was deposited. The law of reflection has been described at least since the hero of Alexandria in the first century AD. Here is a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a little better: The principle that when light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, the incident beam, the reflected beam and the perpendicular to the surface are all in the same plane. Because of this predictability, we can determine the path it will take once it hits a flat surface. Light is known to "behave" in a very predictable way, which is actually a very good thing for us. By reflecting light, concave mirrors emit real and inverted images when the object is blurred, and a virtual, vertical, and magnified image when the object is less than the focal length of the mirror pole.
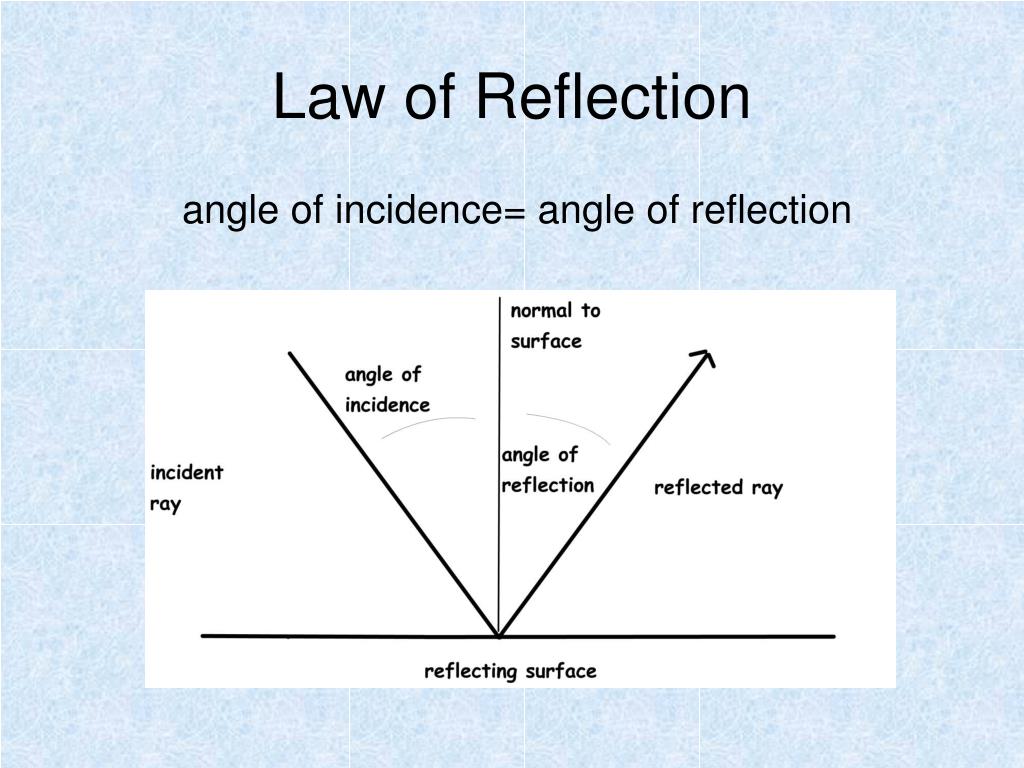
(Both angles are labeled with the Greek letter "theta," accompanied by an index character read "theta-i" for the angle of incidence and "theta-r" for the angle of reflection.) The law of reflection states that when a beam of light is reflected on a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The angle between the reflected beam and the normal is called the reflection angle. The angle between the incident beam and the normal is called the angle of incidence. The normal line divides the angle between the incident beam and the reflected beam into two equal angles. This line is called the normal line (denoted N in the diagram). At the point of incidence where the beam hits the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. The beam of light that leaves the mirror is called the reflected beam (denoted R in the diagram). In the diagram, the beam of light approaching the mirror is called the incident beam (denoted I in the diagram). The reflection angle 0r of a beam is the angle measured from the reflected beam relative to the normal surface. It also indicates that the angle that the incident beam makes with the normal is equal to the angle that the reflected beam makes with the normal. Do you notice how the reflection of the woman looks into the camera, but not the lady herself? (Photo credit: freestockphotos) The law of reflection (in physics) states that when a beam of light hits a flat surface, the incident beam, the reflected beam and the "normal" beam on the mirror surface are all in the same plane.

The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection when light (or other similar forms of energy) hits a smooth surface. Choose the right answer: what is the case with reflection if the second medium is a perfect dielectric? The second law of reflection states that "the incident beam, the perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence, and the reflected beam are all in the same plane." Let`s summarize all this again in scientific language. When the moon reflects from a lake, as shown in Figure 5, a combination of these effects takes place.We first complete the given diagram with the angles of incidence and reflection shown above and also label the incident and reflected rays. A mirror, on the other hand, has a smooth surface (compared with the wavelength of light) and reflects light at specific angles, as illustrated in Figure 4.

Many objects, such as people, clothing, leaves, and walls, have rough surfaces and can be seen from all sides. Diffused light is what allows us to see a sheet of paper from any angle, as illustrated in Figure 3. Since the light strikes different parts of the surface at different angles, it is reflected in many different directions, or diffused. We expect to see reflections from smooth surfaces, but Figure 2 illustrates how a rough surface reflects light. The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 1, which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence- θr = θi.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
